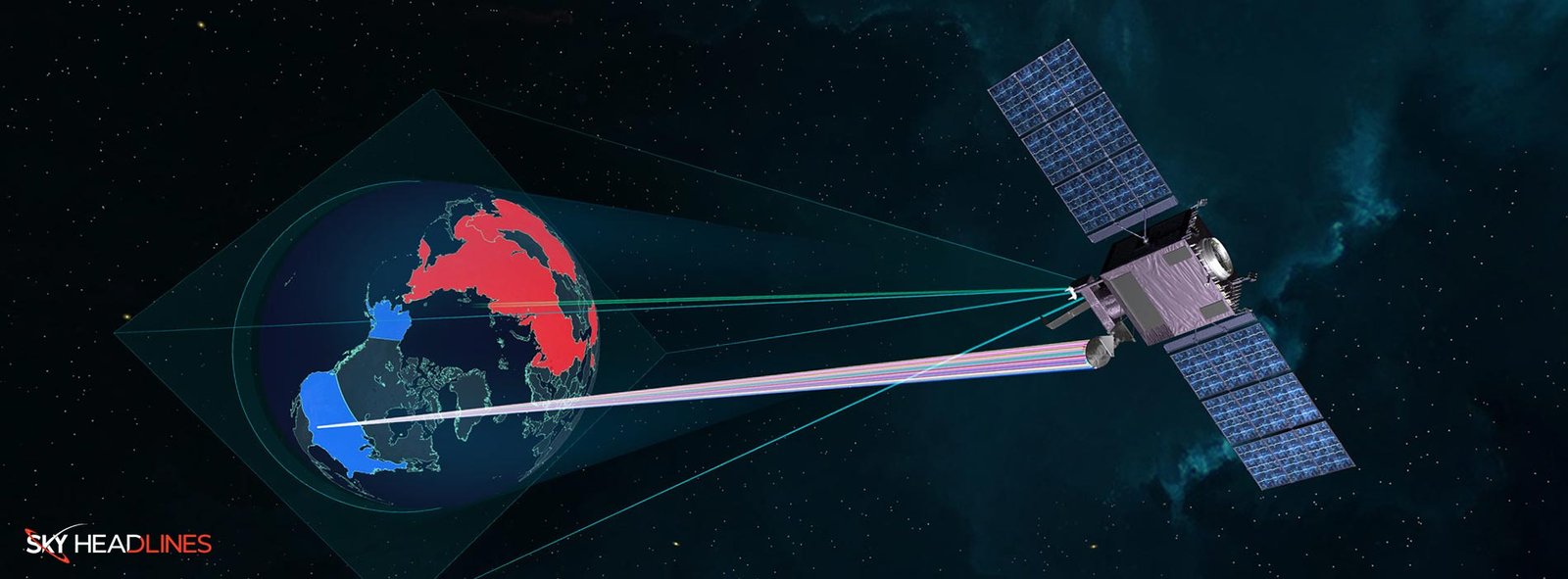
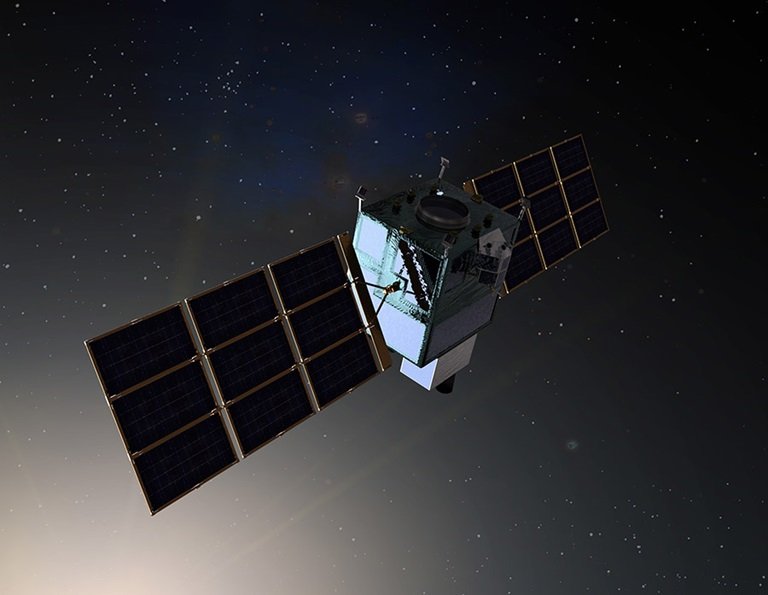
Northrop Grumman is working on the Next Gen Polar (NGP) satellites. It is known as Next-Generation Overhead Persistent Infrared (OPIR). They are significant for the defense of our nation by providing advanced warning against strategic missile threats. Additionally, these satellites cover the northern polar region. Which is the shortest route for missiles to reach the US. But it is a challenging area to monitor from space!

How do the Next Gen Polar Satellites Communicate With Each Other?
NGP satellites follow oval orbits and bring a new level of missile warning. Moreover, their upgraded sensors cover the entire northern hemisphere and have extra resilience to work well even in tough situations.
NGP’s better communication system sends wide-band OPIR data to the ground. This lets us pick out important infrared heat signatures from a lot of data. Therefore by using the improved data, we can fine-tune our processes over time and do better in space.
When a mission is as critical as missile warning and defense, experience and data-driven solutions are essential to high-confidence mission performance.

Shortest Rule for a Ballistic Missile Covering by Next Gen Polar Satellites:
Next-Generation Polar (NGP) are two of the OPIR satellites. They’ll orbit in a stretched-out way and cover the northern polar area. This is the shortest route for a ballistic missile to be aimed at the US. Moreover, the U.S. Space Force hired Northrop Grumman to create these satellites, with Northrop Grumman and Ball Aerospace. These are well structured for the mission payloads. These same groups will also make an extra OPIR payload for the Next-Generation Geo (NGG) satellites. All of these satellites will hang out in the same orbit.
How Next Generation Polar Satellites Detects any Potential Danger?
The NGP satellites work like watchers. They look over a huge part of the Northern Hemisphere and pick up heat signs from ballistic missile launches. These satellites will be about 20,000 miles away in their slightly tilted orbits. When the NGP satellites spot a launch, the Hypersonic and Ballistic Tracking Space Sensor satellites (HBTSS) step in. These other satellites will be closer to Earth. They keep a constant eye on missiles from when they start flying to when they glide in the air. Apart from this, they’ll then give really exact tracking info so we can aim at enemy missiles that are launched from land, sea, or air.
Highly Immersive Virtual Environment Technology for Better Designing of Next Gen Polar Satellites:
On March 14, 2023, in Redondo Beach, California, Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE: NOC) used digital technology. It is called Highly Immersive Virtual Environment (HIVE) to improve the design of the Next-Generation Overhead Persistent Infrared (OPIR) Polar (NGP) satellites.
Northrop Grumman’s HIVE technology lets engineers create, work on. They maintain satellites in a virtual reality setup even before the production of any physical parts. This saves costs and reduces risks during the early development stages. Moreover, they do it through real-time modeling, simulation, visualization, and human interaction.
Carol Erikson, the vice president of Northrop Grumman, says:
“With digital engineering, we can move through the design, testing and manufacturing phases quickly and with agility, saving money and significantly reducing development timelines for large systems.”
In a recent demo using HIVE tech in Redondo Beach, California, Northrop Grumman engineers used virtual reality gear to simulate putting together the satellites’ main parts. This confirmed the NGP design, and digital tech will keep being used in the satellites’ next development stages.
Ciffone said:
“When it comes to detecting ballistic missiles, it’s a mission that can’t fail.”
NGP is a big improvement over the current polar monitoring system called the Space-Based Infrared System in Highly Elliptical Orbit (SBIRS HEO). NGP can spot both hypersonic and regular ballistic missile launches.
Key Features of NGP:
- Northrop Grumman is leveraging digital transformation to deliver capability with speed.
- Model-based systems engineering
- Advanced modeling and simulation
- Updated tools for our business management processes, production, and supply chain management
- End-to-end solutions that enable us to deliver predictable capability at an affordable price
What is the next gen polar?
The Next-Gen OPIR polar satellites are designed to detect the heat signatures of incoming missiles and transmit this data to the ground through a robust and secure communication system.
What is next generation overhead persistent infrared satellites?
As part of Next-Gen OPIR, two NGP satellites will give accurate sensor coverage over the northern hemisphere. Which help to prevent and defend against ballistic and hypersonic missiles.
What is the Northrop Grumman missile warning system?
As part of Next-Gen OPIR, two NGP satellites will give accurate sensor coverage over the northern hemisphere. Therefore, they help to prevent and defend against ballistic and hypersonic missiles.
What is near polar orbit?
Another widely used orbit for remote sensing is the near-polar orbit. Because it has a high angle and its path nearly goes across the poles.
What is next generation overhead persistent infrared polar NGP?
The two NGP satellites will orbit widely and use infrared sensors to detect and track ballistic and hypersonic missiles. They’ll also have an improved communication system to send mission data to the ground, helping decision makers identify heat signatures from incoming threats.
What is the next generation of geostationary weather satellites called?
The GOES-R Series includes four satellites (GOES-R/S/T/U) that will keep the GOES satellite system working until 2036.
What is the difference between geostationary and geosynchronous satellites?
A geostationary orbit is a type of geosynchronous orbit. The difference is that in a geostationary orbit, satellites stay fixed over Earth’s equator, while in a geosynchronous orbit, they can be at any angle.
How NGP is a Significant Part of Next Gen Polar OPIR?
NGP is an indispensable part of the next-gen OPIR construct for numerous reasons:
- It covers the poles. NGP will cover the northern polar region. Which is the shortest route for a ballistic missile to travel toward the United States.
- Failure isn’t an option. Because, the Infrared missile detection strengthens nuclear deterrence and NGP is key to the OPIR construct.
- Near total coverage. According to Sneller, NGP provides round-the-clock coverage of the Northern Hemisphere, including adversarial countries in Eurasia, the Middle East and the Indo-Pacific.
- Resilient. On top of the wide coverage NGP provides from its unique orbit, HEO is more resilient than other orbits.
Sneller, therefore, said:
“NGP monitors virtually every country from which a ballistic or hypersonic missile threat directed at the United States or its allies is likely to originate.”