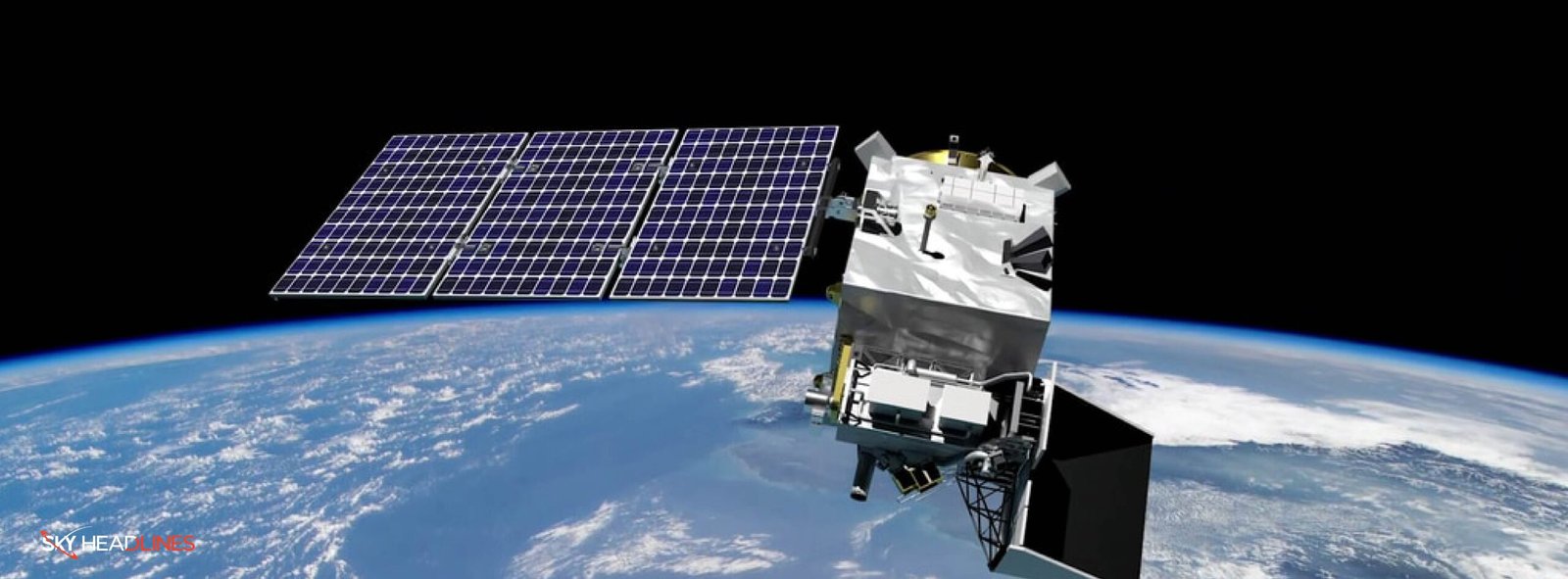
The PACE Satellite is a highly anticipated NASA mission scheduled for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. The launch is targeted for no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on February 6, 2024, from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. This mission is significant as it aims to advance our understanding of Earth’s oceans and atmosphere in the context of a changing climate.
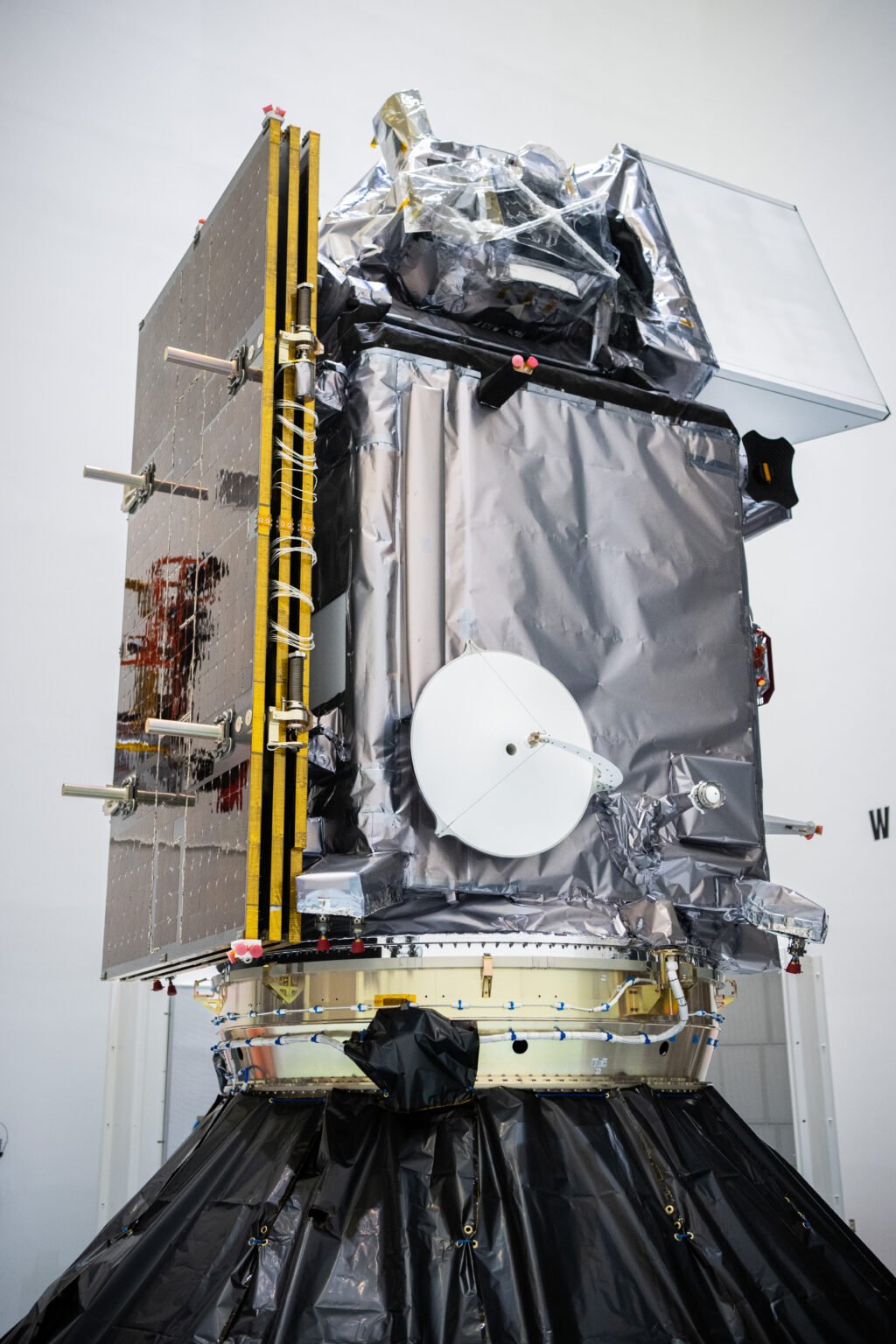

What is the PACE Satellite?
NASA’s PACE Satellite mission, born out of the necessity to monitor and understand the complex interactions between various components of the Earth’s ecosystem, represents a significant leap in satellite-based environmental monitoring. The mission’s primary objective is to observe the interplay among the ocean’s phytoplankton, atmospheric aerosols, and clouds, which are integral to understanding the Earth’s climate system and the impact of human activities on the environment.
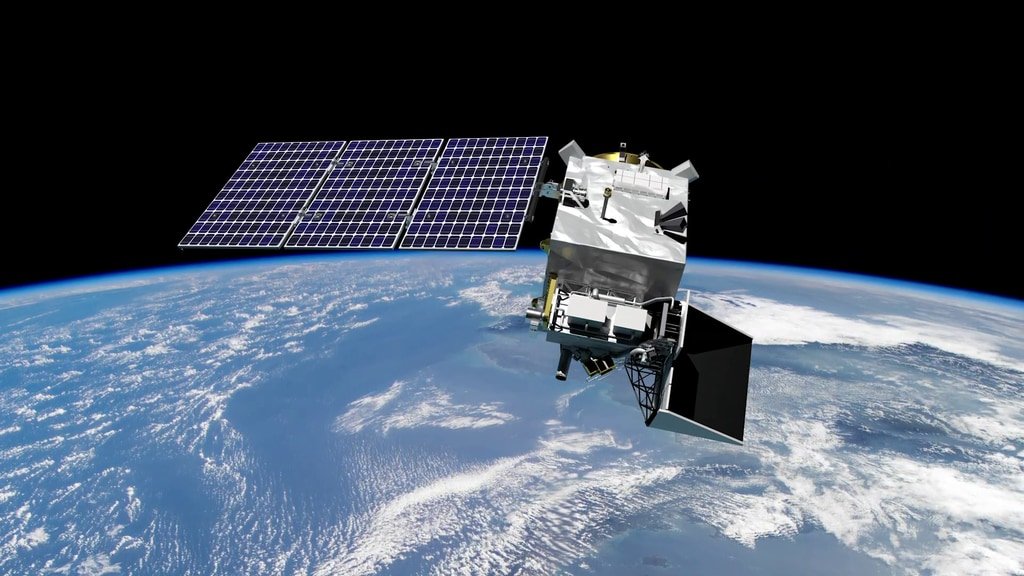

Unraveling the Ocean-Atmosphere Nexus
At the heart of the PACE Satellite mission is the quest to dissect the interactions between oceanic and atmospheric elements. Phytoplankton, microscopic algae dwelling in the ocean, play a crucial role in carbon cycling and are a primary food source within marine ecosystems. PACE will provide essential data on ocean health and its role in the global carbon cycle by monitoring phytoplankton.
The Role of Aerosols and Clouds
Aerosols, tiny particles suspended in the air, including sea salt, smoke, and dust, significantly impact cloud formation and weather patterns. PACE Satellite aims to examine how these particles interact with sunlight and influence cloud properties, thereby affecting the Earth’s energy balance and climate.
Technological Marvels: HARP2 and SPEXone
PACE Satellite is equipped with advanced instruments, notably the two polarimeters, HARP2 and SPEXone, which are pivotal in studying light properties as they interact with aerosols and clouds. HARP2, developed at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County, will observe light from multiple angles, while SPEXone, created by the Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON) and Airbus Netherlands B.V., will provide hyperspectral resolution imaging.
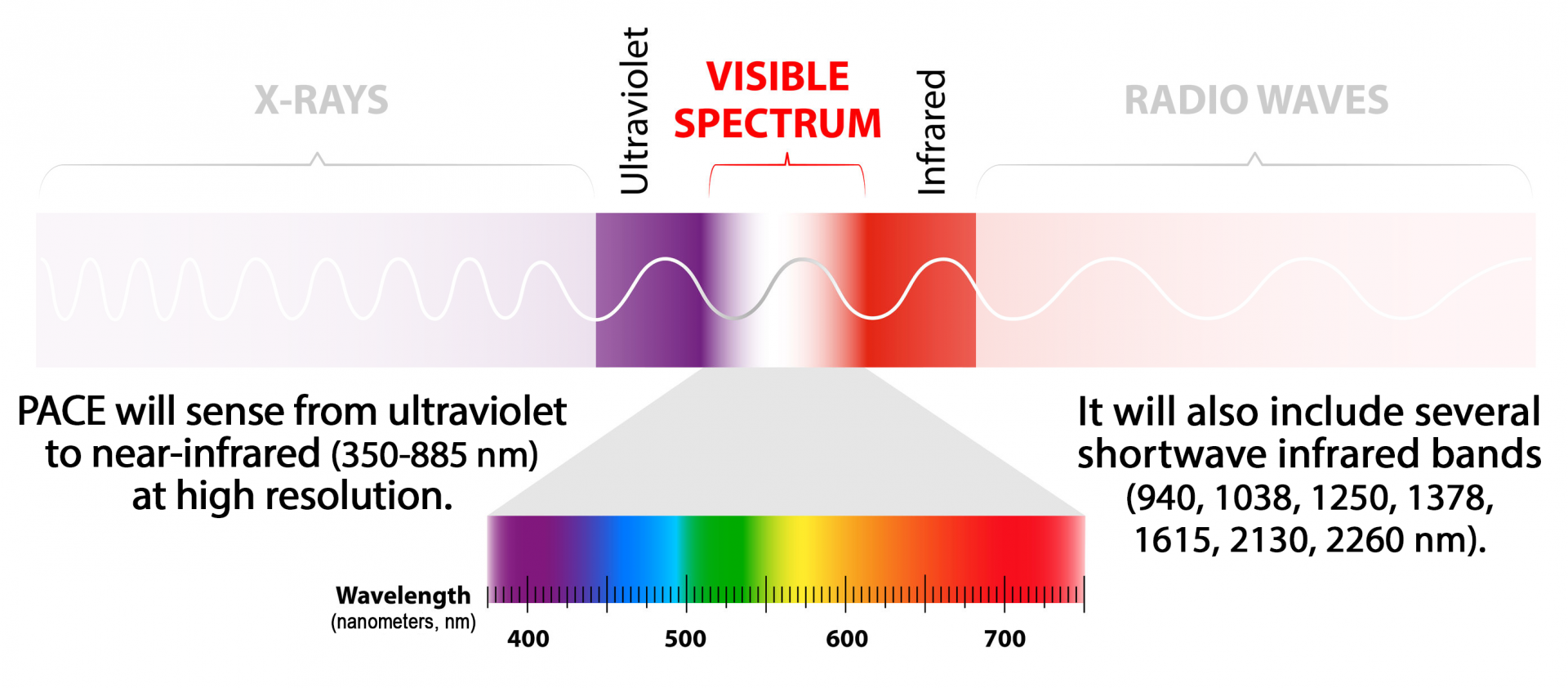
What is the resolution of PACE NASA?
The resolution of NASA’s PACE Satellite mission depends on its instrument:
Ocean Color Instrument (OCI): This instrument has a spatial resolution of 1 kilometer at nadir and a spectral resolution of 5 nanometers. This means it can measure ocean properties with a detail of 1 square kilometer and can distinguish between different colors of light very precisely.
HyperAngular Rainbow Polarimeter – 2 (HARP-2): This instrument has a spatial resolution of 3 kilometers and a spectral resolution ranging from 2 to 30 nanometers depending on the band. It collects measurements from multiple viewing angles, which allows scientists to study the shapes and sizes of aerosols and clouds.
Spectrometer for Planetary EXplorations (SPEXone): This instrument has a spatial resolution of 2.5 kilometers and a spectral resolution of 2 to 4 nanometers, depending on the band. It can also make polarized measurements, which allows scientists to learn more about the composition of aerosols and the properties of land surfaces.
The Anticipated Launch and Operations
The PACE satellite is scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. After launch, it will embark on its mission to scan the Earth every two days, amassing copious data on the chemical composition, movement, and interactions of aerosols and clouds.
How big is the PACE satellite?
The PACE satellite is relatively small compared to other satellites, weighing in at around 1,700 kilograms (3,750 pounds). Its overall size can be described in two ways:
- Height: 1.5 meters (4.9 feet) tall – This is roughly the height of a tall teenager or washing machine.
- Length: 3.2 meters (10.5 feet) long – This is about the length of a small car or pickup truck.
Therefore, although not tiny, the PACE Satellite is quite compact for a spacecraft tasked with such crucial Earth observation missions. Its smaller size compared to some giants like the James Webb Space Telescope helps keep launch costs lower and simplifies certain engineering aspects.
What are PACE’s applications?
PACE Satellite is expected to generate a treasure trove of data that will enhance our understanding of the Earth’s climate system. The satellite will delve into the intricacies of cloud formation, aerosol behavior, and phytoplankton dynamics, offering critical insights into climate change and air quality.
PACE Satellite Contribution to Climate Science
The PACE Satellite mission is more than just another satellite launch; it marks a new chapter in our pursuit of climate knowledge. It will build on NASA’s two-decade legacy of observing ocean biology and will be instrumental in addressing some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
The Global Impact
PACE Satellite observations will have far-reaching implications, aiding policymakers, scientists, and environmentalists worldwide. The mission will provide invaluable data to inform global climate models, enhance our understanding of the Earth’s biosphere, and guide efforts to mitigate the effects of climate change.
The Future Horizon
As the launch date approaches, the excitement within the scientific community is palpable. The PACE Satellite mission is set to embark on a journey that will not only deepen our understanding of our planet but also inspire future generations of scientists and environmental stewards.
PACE Satellite: Collaborations and Outreach
NASA’s collaboration with SpaceX for the PACE Satellite launch exemplifies the growing synergy between government space agencies and private spaceflight companies. Moreover, the mission is expected to foster international scientific cooperation, as the data obtained will be crucial for global environmental monitoring and research.
Conclusion
NASA’s PACE Satellite mission is a testament to human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of knowledge. As we stand on the cusp of this groundbreaking endeavor, we are reminded of our responsibility to understand and protect our planet. PACE is not just a mission; it’s a beacon of hope, signaling a new era of environmental stewardship and scientific discovery.